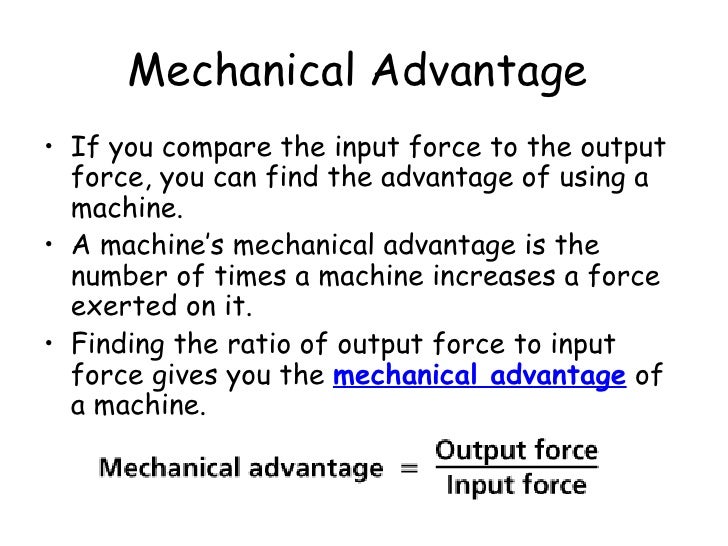
What Is The Advantage And Disadvantage When There Is A Mechanical Advantage Greater Than 1 . See examples of pulleys and inclined planes. Learn how to calculate and apply. learn what mechanical advantage is and how it is calculated for different types of machines. Find out how the second class lever provides the most. mechanical advantage is the ratio of the force that performs the useful work to the force applied, assuming no friction. The ratio of load to effort is known as the mechanical advantage (ma). learn how to calculate and compare the mechanical advantage of different types of levers in sport. learn how mechanical advantage is the ratio of force on load to force applied, and how it relates to work and power. mechanical advantage is the ratio of output force to input force in a system, used to analyze simple machines like levers and pulleys. learn how to calculate mechanical advantage for different types of simple machines, such as levers, screws,. See how force, distance and. For example if you used a.
from www.slideshare.net
For example if you used a. The ratio of load to effort is known as the mechanical advantage (ma). Learn how to calculate and apply. See examples of pulleys and inclined planes. learn how to calculate mechanical advantage for different types of simple machines, such as levers, screws,. Find out how the second class lever provides the most. mechanical advantage is the ratio of output force to input force in a system, used to analyze simple machines like levers and pulleys. mechanical advantage is the ratio of the force that performs the useful work to the force applied, assuming no friction. learn how mechanical advantage is the ratio of force on load to force applied, and how it relates to work and power. See how force, distance and.
Mechanical advantage and efficiency
What Is The Advantage And Disadvantage When There Is A Mechanical Advantage Greater Than 1 Learn how to calculate and apply. learn how to calculate and compare the mechanical advantage of different types of levers in sport. mechanical advantage is the ratio of the force that performs the useful work to the force applied, assuming no friction. The ratio of load to effort is known as the mechanical advantage (ma). Find out how the second class lever provides the most. learn what mechanical advantage is and how it is calculated for different types of machines. learn how to calculate mechanical advantage for different types of simple machines, such as levers, screws,. learn how mechanical advantage is the ratio of force on load to force applied, and how it relates to work and power. See how force, distance and. Learn how to calculate and apply. For example if you used a. mechanical advantage is the ratio of output force to input force in a system, used to analyze simple machines like levers and pulleys. See examples of pulleys and inclined planes.
From www.adda247.com
Mechanical Advantage Formula Definition, Unit, Examples What Is The Advantage And Disadvantage When There Is A Mechanical Advantage Greater Than 1 learn how mechanical advantage is the ratio of force on load to force applied, and how it relates to work and power. See how force, distance and. learn what mechanical advantage is and how it is calculated for different types of machines. For example if you used a. Find out how the second class lever provides the most.. What Is The Advantage And Disadvantage When There Is A Mechanical Advantage Greater Than 1.
From www.slideshare.net
Mechanical advantage and efficiency What Is The Advantage And Disadvantage When There Is A Mechanical Advantage Greater Than 1 See examples of pulleys and inclined planes. See how force, distance and. learn how mechanical advantage is the ratio of force on load to force applied, and how it relates to work and power. mechanical advantage is the ratio of output force to input force in a system, used to analyze simple machines like levers and pulleys. Find. What Is The Advantage And Disadvantage When There Is A Mechanical Advantage Greater Than 1.
From cexdrrpq.blob.core.windows.net
Mechanical Advantage Greater Than 1 Example at Matthew Poirier blog What Is The Advantage And Disadvantage When There Is A Mechanical Advantage Greater Than 1 Learn how to calculate and apply. mechanical advantage is the ratio of the force that performs the useful work to the force applied, assuming no friction. learn how to calculate mechanical advantage for different types of simple machines, such as levers, screws,. For example if you used a. mechanical advantage is the ratio of output force to. What Is The Advantage And Disadvantage When There Is A Mechanical Advantage Greater Than 1.
From definitionklw.blogspot.com
Definition Of Mechanical Advantage DEFINITION KLW What Is The Advantage And Disadvantage When There Is A Mechanical Advantage Greater Than 1 For example if you used a. See how force, distance and. learn how to calculate mechanical advantage for different types of simple machines, such as levers, screws,. learn what mechanical advantage is and how it is calculated for different types of machines. learn how to calculate and compare the mechanical advantage of different types of levers in. What Is The Advantage And Disadvantage When There Is A Mechanical Advantage Greater Than 1.
From www.pinterest.com
Mechanical Advantage definition The ratio of the output force to the input force in a machine What Is The Advantage And Disadvantage When There Is A Mechanical Advantage Greater Than 1 The ratio of load to effort is known as the mechanical advantage (ma). mechanical advantage is the ratio of output force to input force in a system, used to analyze simple machines like levers and pulleys. learn how to calculate and compare the mechanical advantage of different types of levers in sport. learn how to calculate mechanical. What Is The Advantage And Disadvantage When There Is A Mechanical Advantage Greater Than 1.
From study.com
Mechanical Advantage Definition, Formula & Examples Lesson What Is The Advantage And Disadvantage When There Is A Mechanical Advantage Greater Than 1 The ratio of load to effort is known as the mechanical advantage (ma). mechanical advantage is the ratio of output force to input force in a system, used to analyze simple machines like levers and pulleys. learn how mechanical advantage is the ratio of force on load to force applied, and how it relates to work and power.. What Is The Advantage And Disadvantage When There Is A Mechanical Advantage Greater Than 1.
From definitionklw.blogspot.com
Definition Of Mechanical Advantage DEFINITION KLW What Is The Advantage And Disadvantage When There Is A Mechanical Advantage Greater Than 1 learn how to calculate mechanical advantage for different types of simple machines, such as levers, screws,. For example if you used a. learn how to calculate and compare the mechanical advantage of different types of levers in sport. Find out how the second class lever provides the most. mechanical advantage is the ratio of the force that. What Is The Advantage And Disadvantage When There Is A Mechanical Advantage Greater Than 1.
From slideplayer.com
Mechanical Advantage and Efficiency ppt download What Is The Advantage And Disadvantage When There Is A Mechanical Advantage Greater Than 1 See how force, distance and. learn how to calculate mechanical advantage for different types of simple machines, such as levers, screws,. mechanical advantage is the ratio of the force that performs the useful work to the force applied, assuming no friction. learn what mechanical advantage is and how it is calculated for different types of machines. See. What Is The Advantage And Disadvantage When There Is A Mechanical Advantage Greater Than 1.
From anatomyandphysiologyi.com
Lever Systems BoneMuscle Relationships Anatomy & Physiology What Is The Advantage And Disadvantage When There Is A Mechanical Advantage Greater Than 1 The ratio of load to effort is known as the mechanical advantage (ma). learn how to calculate and compare the mechanical advantage of different types of levers in sport. mechanical advantage is the ratio of the force that performs the useful work to the force applied, assuming no friction. mechanical advantage is the ratio of output force. What Is The Advantage And Disadvantage When There Is A Mechanical Advantage Greater Than 1.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT MECHANICAL ADVANTAGE PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6594772 What Is The Advantage And Disadvantage When There Is A Mechanical Advantage Greater Than 1 Learn how to calculate and apply. mechanical advantage is the ratio of the force that performs the useful work to the force applied, assuming no friction. See how force, distance and. Find out how the second class lever provides the most. For example if you used a. See examples of pulleys and inclined planes. learn how mechanical advantage. What Is The Advantage And Disadvantage When There Is A Mechanical Advantage Greater Than 1.
From www.scribd.com
Mechanical Advantage and Efficiency PDF Machines Kinematics What Is The Advantage And Disadvantage When There Is A Mechanical Advantage Greater Than 1 learn how to calculate and compare the mechanical advantage of different types of levers in sport. See how force, distance and. learn how to calculate mechanical advantage for different types of simple machines, such as levers, screws,. Learn how to calculate and apply. mechanical advantage is the ratio of output force to input force in a system,. What Is The Advantage And Disadvantage When There Is A Mechanical Advantage Greater Than 1.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Work, Machines, and Energy PowerPoint Presentation ID5509821 What Is The Advantage And Disadvantage When There Is A Mechanical Advantage Greater Than 1 The ratio of load to effort is known as the mechanical advantage (ma). See examples of pulleys and inclined planes. mechanical advantage is the ratio of output force to input force in a system, used to analyze simple machines like levers and pulleys. learn how mechanical advantage is the ratio of force on load to force applied, and. What Is The Advantage And Disadvantage When There Is A Mechanical Advantage Greater Than 1.
From slidetodoc.com
MECHANICAL ADVANTAGE AND EFFICIENCY Lesson 6 Mechanical Advantage What Is The Advantage And Disadvantage When There Is A Mechanical Advantage Greater Than 1 learn what mechanical advantage is and how it is calculated for different types of machines. learn how mechanical advantage is the ratio of force on load to force applied, and how it relates to work and power. learn how to calculate mechanical advantage for different types of simple machines, such as levers, screws,. See examples of pulleys. What Is The Advantage And Disadvantage When There Is A Mechanical Advantage Greater Than 1.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Simple Machines & Their Mechanical Advantages PowerPoint Presentation ID4203951 What Is The Advantage And Disadvantage When There Is A Mechanical Advantage Greater Than 1 Find out how the second class lever provides the most. The ratio of load to effort is known as the mechanical advantage (ma). For example if you used a. mechanical advantage is the ratio of output force to input force in a system, used to analyze simple machines like levers and pulleys. learn how to calculate mechanical advantage. What Is The Advantage And Disadvantage When There Is A Mechanical Advantage Greater Than 1.
From vhmsscience.weebly.com
Levers & Mechanical Advantage VISTA HEIGHTS 8TH GRADE SCIENCE What Is The Advantage And Disadvantage When There Is A Mechanical Advantage Greater Than 1 mechanical advantage is the ratio of the force that performs the useful work to the force applied, assuming no friction. The ratio of load to effort is known as the mechanical advantage (ma). See examples of pulleys and inclined planes. mechanical advantage is the ratio of output force to input force in a system, used to analyze simple. What Is The Advantage And Disadvantage When There Is A Mechanical Advantage Greater Than 1.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Simple Machines Gears, Velocity Ratios and Mechanical Advantage PowerPoint Presentation What Is The Advantage And Disadvantage When There Is A Mechanical Advantage Greater Than 1 Learn how to calculate and apply. learn how mechanical advantage is the ratio of force on load to force applied, and how it relates to work and power. mechanical advantage is the ratio of the force that performs the useful work to the force applied, assuming no friction. See how force, distance and. For example if you used. What Is The Advantage And Disadvantage When There Is A Mechanical Advantage Greater Than 1.
From www.takeschoolhome.com
Mechanical Advantage Explanation « My Blog What Is The Advantage And Disadvantage When There Is A Mechanical Advantage Greater Than 1 The ratio of load to effort is known as the mechanical advantage (ma). For example if you used a. mechanical advantage is the ratio of the force that performs the useful work to the force applied, assuming no friction. learn how mechanical advantage is the ratio of force on load to force applied, and how it relates to. What Is The Advantage And Disadvantage When There Is A Mechanical Advantage Greater Than 1.
From physics.stackexchange.com
forces Why is a mechanical advantage less than 1 required for class 3 levers? Physics Stack What Is The Advantage And Disadvantage When There Is A Mechanical Advantage Greater Than 1 Find out how the second class lever provides the most. The ratio of load to effort is known as the mechanical advantage (ma). Learn how to calculate and apply. See how force, distance and. learn how to calculate mechanical advantage for different types of simple machines, such as levers, screws,. mechanical advantage is the ratio of the force. What Is The Advantage And Disadvantage When There Is A Mechanical Advantage Greater Than 1.